The IVF process step by step
August 16, 2024Pregnancy is not always easy. Luckily there are multiple solutions to build a family and In vitro Fertilization is one of them, especially if the couple suffers from infertility. IVF has led to the birth of around 10 million babies until now since the first successful operation in 1978. So how does it work?
-
Preparation
Preparation for IVF sometimes begins months before the procedure. First, the medical team takes the necessary medical information and requests the necessary tests for the husband and wife. Sometimes, birth control pills or estrogen may be prescribed to control the timing of the menstrual cycle.
-
Ovarian stimulation
During a normal menstrual cycle, only one egg matures. During the IVF process, hormone injections are used to increase the number of mature eggs and increase the chances of pregnancy. The type of treatment, dosage and protocol are decided by the doctor according to your specific condition. This stage requires one or two visits to the center during which an ultrasound scan is taken to monitor the size of the eggs and the ovarian response to the treatment. When the eggs reach the required size, the trigger shot is given. The timing of this injection is very important, and the egg retrieval must be performed exactly 36 hours later.
-
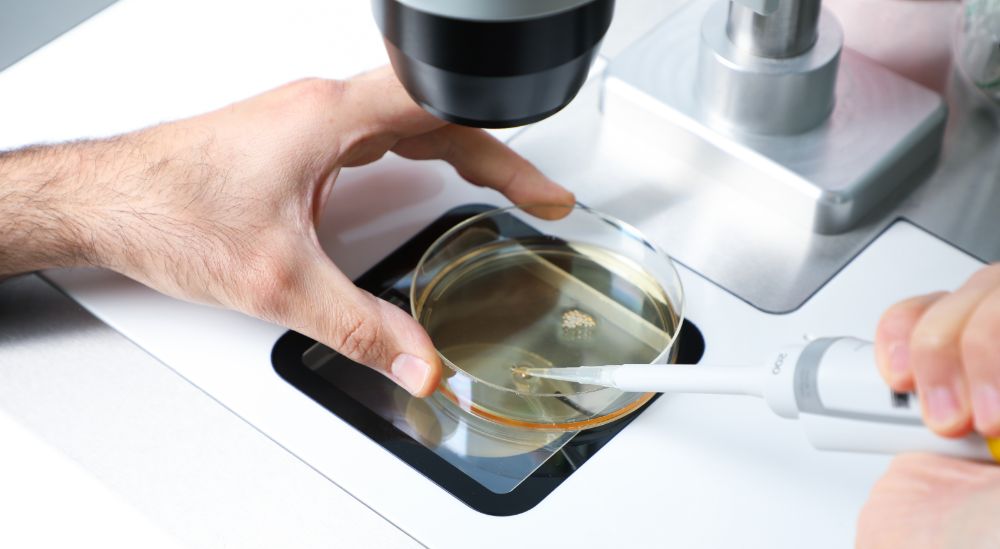
Egg retrieval
During this step, a suction device attached to a long, thin needle is inserted through the vagina. Using this device, the doctor withdraws all the mature eggs one by one. The extracted eggs are placed in a culture dish inside an incubator in the laboratory. The retrieval process is performed under local anesthesia and is not painful.
-
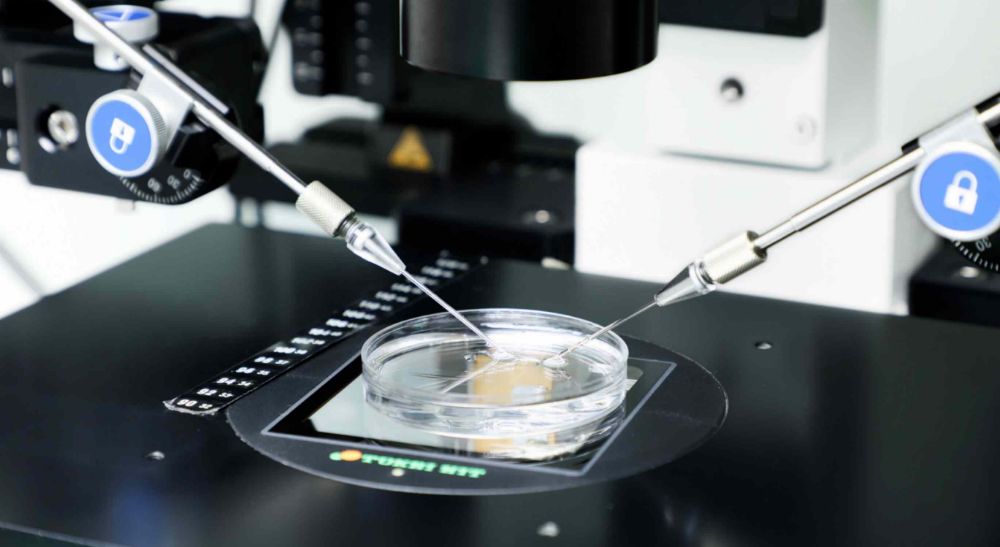
Fertilization
Egg fertilization takes place on the same day of the retrieval procedure. It is possible to use the regular fertilization method (IVF) or to use intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), which involves introducing one sperm into each mature egg. About 70% of mature eggs are successfully fertilized and result in embryos, this is called the fertilization rate.
-
Embryo culture
During this period, the embryos develop and divide in the laboratory and are monitored for several days, ranging from two to seven days. Generally, half of the embryos will develop into grade I and will be suitable for transfer to the uterus. Good embryos can be transferred directly or frozen and transferred in a subsequent cycle.
-
Embryo transfer
If the Doctor decides to perform a fresh transfer, the transfer process will take place a few days after fertilization. This process is short and easy and is similar to any regular gynecological examination, so it does not require any anesthesia. A speculum is placed inside the vagina and a thin catheter is inserted through the cervix. The embryos are then injected through the catheter into the uterus. The surplus embryos are frozen in the laboratory. After the embryo transfer, the woman may feel symptoms such as bloating, mild cramps, chest pain, slight bleeding or constipation. These symptoms are caused by hormones and not the embryos themselves, so it is not possible to know whether implantation has occurred or not.
-
Pregnancy test
A blood pregnancy test is performed approximately two weeks after the embryo transfer. If the result of the pregnancy test is positive, a normal pregnancy follow up begins. The success rate of IVF varies according to the age of the woman. If the pregnancy result is negative, an attempt can be made to transfer embryos. Again, in most cases, frozen surplus embryos are used. If no excess embryos are obtained, you can repeat the IVF procedure as soon as you are ready for it. Best of Luck!